Blog
Improvements and Challenges
The Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region continues to evolve as a dynamic player in the global supply chain arena. Despite ongoing political and economic challenges, the region is experiencing notable transformations driven by infrastructure investments, technological innovation, and increasing regional cooperation. As global trade patterns shift in response to geopolitical, economic, and environmental forces, understanding the developments shaping MENA’s supply chain ecosystem is essential for stakeholders with interests in or connected to the region.
Table of Contents
Progress in the MENA Supply Chain Landscape
Technological Integration
Technological innovation is becoming a key enabler of supply chain efficiency in the region. MENA-based businesses are increasingly adopting automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain technologies to optimize logistics operations. Predictive analytics, AI-driven demand forecasting, and smart warehouse management systems are helping firms better anticipate market fluctuations and improve operational resilience.
Enhanced Regional Connectivity
Efforts to foster intra-regional trade have gained momentum, supported by frameworks such as the Greater Arab Free Trade Area (GAFTA). Combined with MENA’s strategic geographic position—linking Asia, Europe, and Africa—these trade agreements are strengthening the region’s role in global commerce. Improved diplomatic relations and cross-border infrastructure projects further support regional integration and trade facilitation.

Persistent Challenges in the Region
Political and Geopolitical Instability
Despite positive developments, political volatility continues to pose significant risks to supply chain continuity. Ongoing conflicts in countries such as Syria, Libya, and Yemen have disrupted trade routes and increased operational risks. Even in relatively stable states, geopolitical tensions—such as diplomatic rifts or sudden policy changes—can hinder long-term planning and investment.
Uneven Infrastructure Quality
While flagship logistics projects in key Gulf countries are world-class, other parts of the region continue to suffer from underdeveloped or outdated infrastructure. Transportation bottlenecks, poor road connectivity, and limited rail access in rural or conflict-affected areas present significant hurdles to efficient supply chain operations.
Economic Dependence on Fossil Fuels
The region’s long-standing reliance on oil and gas revenues continues to shape its economic structure and transport logistics. As the global economy transitions toward renewable energy sources, MENA nations face pressure to diversify their economies. Within logistics, this means adapting to future energy needs—such as electrification of fleets or investment in alternative fuels—which will require substantial strategic planning and capital investment.
Labor Market Pressures
Labor dynamics also present challenges. Many supply chains in the region are heavily dependent on low-cost migrant labor, particularly in warehousing and transportation. Efforts by Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states to nationalize labor markets—aimed at increasing employment among citizens—could lead to skill gaps or labor shortages in logistics and manufacturing, unless balanced with upskilling initiatives.

Copyrights: iStock
Opportunities for Strategic Improvement
Economic Diversification
Governments across the MENA region are investing in sectors such as manufacturing, technology, and e-commerce to reduce dependence on oil exports. These initiatives, including Vision 2030 in Saudi Arabia and the UAE’s We the UAE 2031, provide new avenues for supply chain expansion and modernization. A more diversified economy will likely lead to more stable and resilient logistics ecosystems.
Regional Integration and Trade Harmonization
Increased cooperation between MENA nations could significantly improve the region’s logistics efficiency. Harmonizing customs procedures, reducing non-tariff barriers, and investing in cross-border infrastructure would streamline the movement of goods. Deeper integration could also boost foreign direct investment and promote regional value chains.
Sustainability and Green Logistics
As sustainability becomes a global priority, there is growing interest in decarbonizing logistics operations in the region. Initiatives such as green ports, low-emission transport corridors, and renewable energy-powered warehouses are being explored. Sustainability efforts not only align with global standards but also enhance competitiveness by attracting environmentally conscious partners and investors.

Positioning the MENA as a Global Logistics Hub
The MENA region stands at a pivotal moment in its supply chain evolution. While structural challenges—such as political instability, infrastructure disparity, and oil dependency—continue to impede progress, there is also strong momentum toward reform and modernization. Investments in infrastructure, digital technologies, and sustainability, alongside broader economic diversification efforts, are positioning the region as an emerging hub for global logistics.
For businesses operating within or trading with the region, staying abreast of these shifts—and building supply chain strategies that are agile, resilient, and adaptive—will be key to seizing opportunities and mitigating risks in 2025 and beyond.
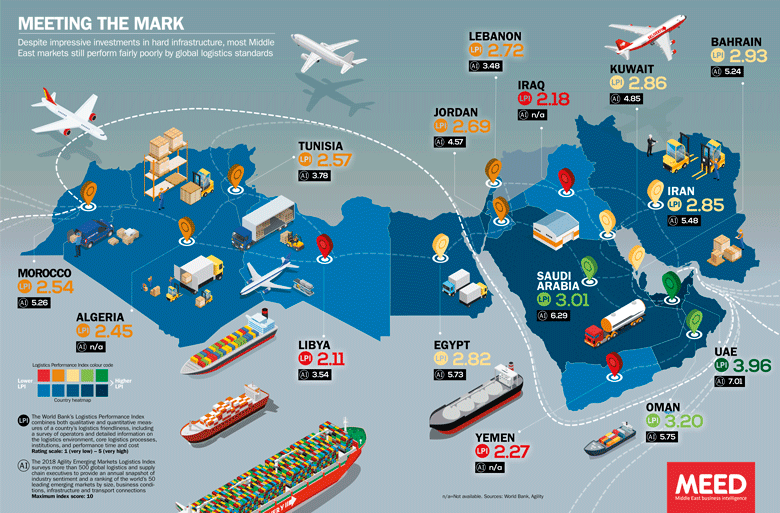
Copyrights: MEED (2019), How the region's logistics sector is performing, Middle East Business Intelligence